Radioactive Waste
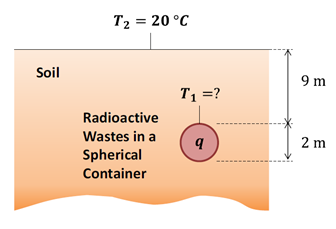
Consider radioactive waste that is stored in a spherical container, buried 9 m below the earth’s surface. The thermal conductivity of the soil can be assumed as 0.52 W/m∙K. The container’s outside diameter is 2 m (D), and 1500 W of heat (q) is released as a result of radioactive decay. If the soil surface temperature is kept at 20°C, what is the outside surface temperature of the container under steady state conditions?
Expand Hint
Hint 2
Thermal resistance:
$$$q=Sk(T_1-T_2)$$$
where
$$S$$
is the shape factor,
$$k$$
is the thermal conductivity, and
$$T$$
is the temperature.
Thermal resistance:
$$$q=Sk(T_1-T_2)$$$
where
$$S$$
is the shape factor,
$$k$$
is the thermal conductivity, and
$$T$$
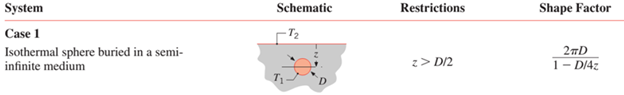
is the temperature. To determine shape factor, referencing a heat transfer equation table. The problem scenario qualifies as an isothermal sphere buried in a semi-infinite medium by meeting the below conditions:
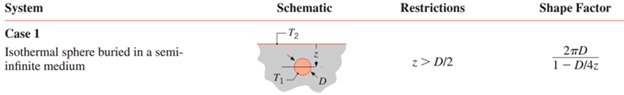
As a result, the heat transfer equation is:
$$$q=\frac{2\pi D}{1-\frac{D}{4z}}k(T_1-T_2)$$$
$$$=\frac{2\pi (2m)}{1-\frac{2m}{4(10m)}}(0.52W/mK)(T_1-20^{\circ}C)$$$
$$$q=(6.87\:W/K)(T_1-20^{\circ}C)=1500\:W$$$
Thus:
$$$T_1=\frac{1500W}{6.87\frac{W}{K}}+20^{\circ}C=238^{\circ}C$$$
238°C
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked