Heat Transfer Modes
Describe the fundamental modes of heat transfer.
Expand Hint
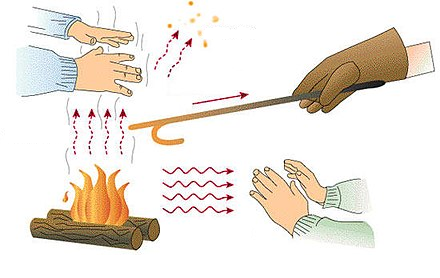
Conduction
: the process in which heat flows from objects with higher temperature to objects with lower temperature on a microscopic atom level due to high speed particles crashing into low speed particles, which increases their overall kinetic energy.
Convection
: the movement of fluid causing heat to transfer from one location to another.
Radiation
: electromagnetic waves carrying energy from an emitting body through a vacuum (unlike the other modes), or a transparent medium (solid or liquid).
Advection
: the transfer of heat through bulk motion of a fluid or gas (not possible in solids). There are a lot of parallels with convection, but the main distinction is advection is solely dependent on the currents within a fluid, while convection is a broader process. Convection may contain advection, but not all advection transfers are thermal convections by definition.
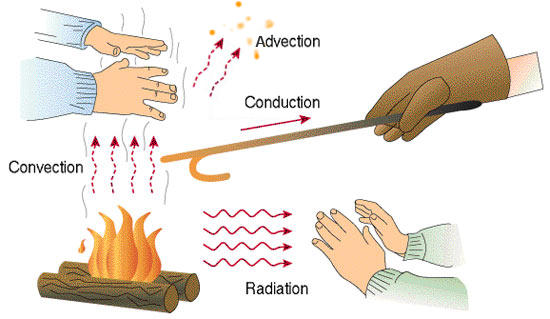
Conduction
: the process in which heat flows from objects with higher temperature to objects with lower temperature on a microscopic atom level due to high speed particles crashing into low speed particles, which increases their overall kinetic energy.
Convection
: the movement of fluid causing heat to transfer from one location to another.
Radiation
: electromagnetic waves carrying energy from an emitting body through a vacuum (unlike the other modes), or a transparent medium (solid or liquid).
Advection
: the transfer of heat through bulk motion of a fluid or gas (not possible in solids).
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked