P-h Diagram
Refrigerant HFC-134a is used for a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle. If the evaporator temperature is 40°C, and the condenser temperature is 60°C, what is the evaporator cooling in kJ/kg?
Expand Hint
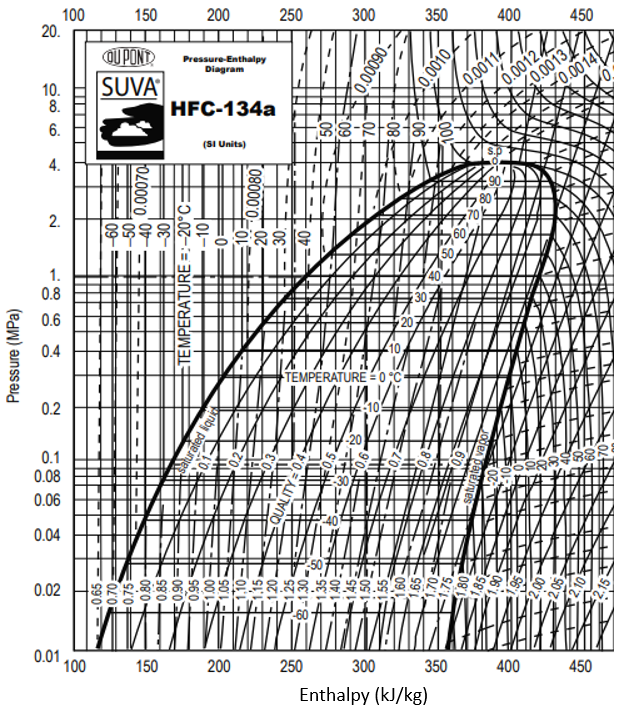
For this specific problem, the pressure vs enthalpy diagram is:
Hint 2
For Boilers, Condensers, and Evaporators:
$$$h_{in}+q=h_{exit}$$$
where
$$h$$
is specific enthalpy, and
$$q$$
is the heat transfer per unit mass.
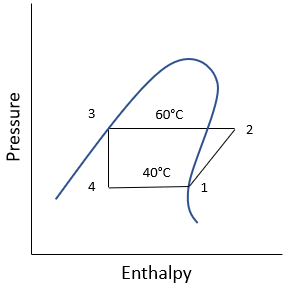
For this specific problem, the pressure vs enthalpy diagram is:
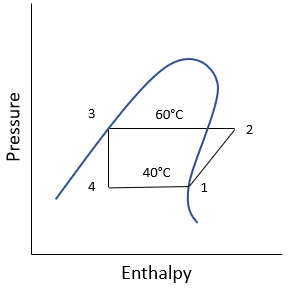
For Boilers, Condensers, and Evaporators:
$$$h_{in}+q=h_{exit}$$$
where
$$h$$
is specific enthalpy, and
$$q$$
is the heat transfer per unit mass. Per the problem statement’s P-h diagram:
$$$q_{evaporator}=h_{1}-h_{4}$$$
In the P-h diagram for Refrigerant HFC-134a, the enthalpy associated with the evaporator’s 40°C temperature intersecting with the saturated vapor curve (1) is
$$h_1$$
(2). The enthalpy associated with condenser’s 60°C intersecting with the saturated liquid curve (3) is
$$h_3$$
(4).
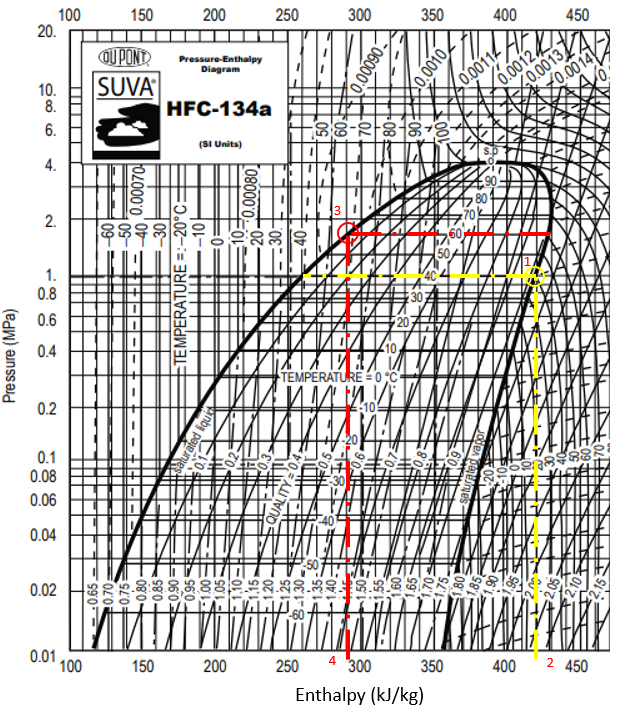
Because
$$h_3=h_4$$
based on the vapor-compression refrigeration cycle:
$$$q_{evaporator}=430\frac{kJ}{kg}-290\frac{kJ}{kg}=140\:\frac{kJ}{kg}$$$
140 kJ/kg
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked
Similar Problems from FE Sub Section: State Functions, P-h Diagrams
Similar Problems from FE Section: Properties of Single-Component Systems
224. Two-Phase Systems