Find the Heat Transfer and Flux
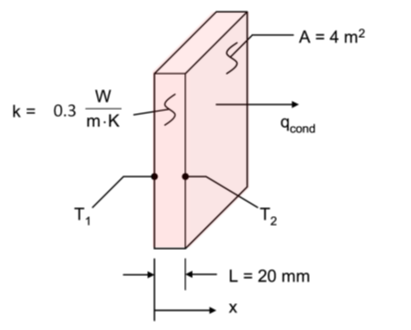
The below rectangular sheet of rigid insulation has a thermal conductivity of k = 0.3 W/m∙K, and experiences a temperature difference of T1-T2=10K across its 20-mm-thick material face sheet.
- What is the heat flux through a 2 m x 2 m sheet of the insulation in W/m^2?
- What is the rate of heat transfer (W) through the sheet of insulation?
Expand Hint
Heat flux is:
$$$q_x"=-k\frac{dT}{dx}=k\frac{T_1-T_2}{L}$$$
where
$$k$$
is the thermal conductivity,
$$dT$$
is the change in temperature, and
$$dx$$
is the distance.
Hint 2
Fourier’s Law of Conduction:
$$$q_x=q_x"\times A$$$
where
$$q_x$$
is the rate of heat transfer,
$$q_x"$$
is the heat flux, and
$$A$$
is the area.
ASSUMPTIONS
: (1) One-dimensional conduction in the x-direction, (2) Steady-state conditions, (3) Constant properties.
The heat flux equation is:
$$$q_x"=-k\frac{dT}{dx}=k\frac{T_1-T_2}{L}$$$
where
$$k$$
is the thermal conductivity,
$$dT$$
is the change in temperature, and
$$dx$$
is the distance. Solving,
$$$q_x"=0.3\frac{W}{m\cdot K}\times \frac{10K}{0.02m}=150\: \frac{W}{m^2}$$$
Fourier’s Law of Conduction:
$$$q_x=q_x"\times A$$$
where
$$q_x$$
is the rate of heat transfer,
$$q_x"$$
is the heat flux, and
$$A$$
is the area. Thus, the heat rate is:
$$$q_x=150\frac{W}{m^2}\times 4m^2=600\: W$$$
- $$150\: \frac{W}{m^2}$$
- $$600\:W$$
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked
Similar Problems from FE Sub Section: Conduction
006. How does CPU Cooling Work?
046. Electrical Heater Rod
062. Cooling a CPU
301. Brick Wall
562. Heat Transfer Area
607. Heating Distance
Similar Problems from FE Section: Basic Heat-Transfer Rate Equations
006. How does CPU Cooling Work?
045. A Steam Pipe
046. Electrical Heater Rod
062. Cooling a CPU
093. Convection and Velocity
203. Heat Transfer Rate
212. Heat Transferring
255. Heat Transfer
301. Brick Wall
493. Heat Transfer Coefficient
497. Change in Temp
561. Radiation
562. Heat Transfer Area
607. Heating Distance
659. Radiation Temp