Oil Bath Quenching
A 60 mm diameter bar stock made from 4340 steel is quenched in an agitated oil bath. What is the expected hardness (R_c) at the bar stock's center?
Expand Hint
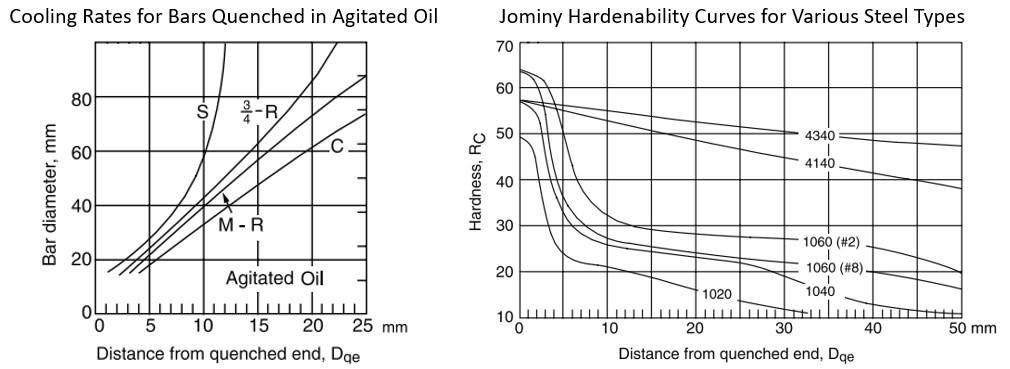
Quenching is rapidly cooling a workpiece in water, oil, or air to obtain certain material properties. When looking at the cooling rates for bars quenched in agitated oil graph, we need to find the
$$D_{qe}$$
that is associated with our given bar stock diameter intersecting the center cooling curve C.
Hint 2
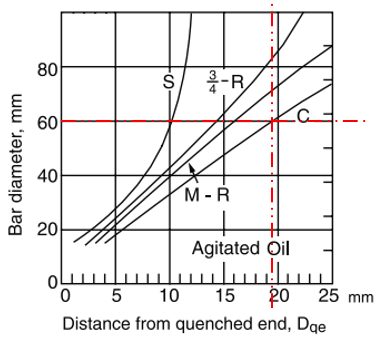
Quenching is rapidly cooling a workpiece in water, oil, or air to obtain certain material properties. When looking at the cooling rates for bars quenched in agitated oil graph, we need to find the
$$D_{qe}$$
that is associated with our given bar stock diameter intersecting the center cooling curve C.
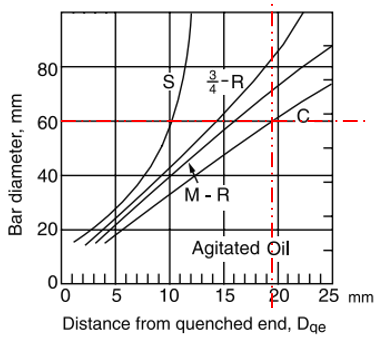
The distance from quenched end,
$$D_{qe}$$
, for a 60 mm quenched in agitated oil is around 19.5 mm. This can be used to determine the 4340 hardness via the Jominy end-quench test, which is a standardized method of measuring the hardenability of steels.
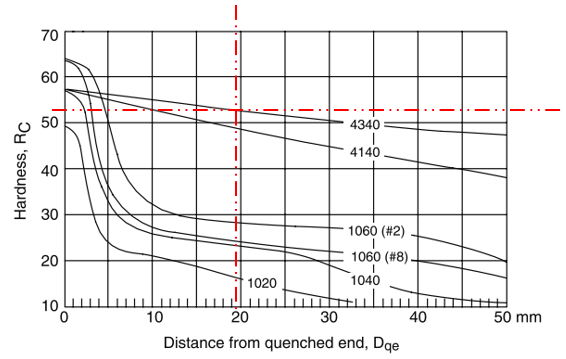
On the Jominy Curve, the 19.5 mm distance from the quenched end intersects the 4340 steel line at around
$$R_c=52$$
. Thus, the expected center hardness for a 4340 steel of diameter 60 mm when quenched in an agitated oil bath is 52.
52
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked
Similar Problems from FE Section: Hardenability
035. Material Testing
231. Subway Hand Rail
403. Train Tracks
641. Concrete Strength