Turbine Power
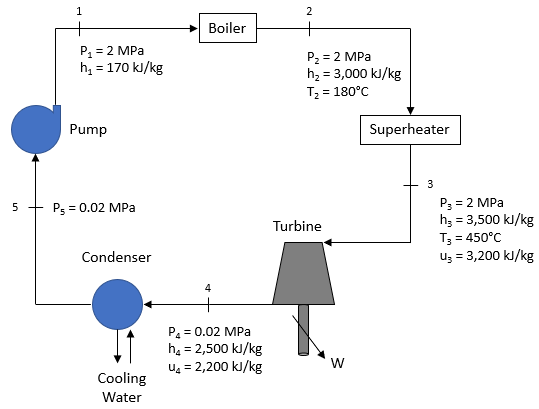
The Rankine cycle below is used to power a plant complex with water as the working fluid. If the fluid’s mass flow rate is 25 kg/s, what is the turbine’s output power in MW? Assume steady state and steady flow conditions. Also, disregard pressure losses and kinetic/potential energy effects. Note the density of water is 1,000 kg/m^3.
Expand Hint
Turbines, Pumps, and Compressors are often considered adiabatic (no heat transfer), so in a steady-state and steady-flow conditions:
$$$h_{in}=h_{exit}+w$$$
where
$$h$$
is specific enthalpy, and
$$w$$
is the turbine work per unit mass.
Hint 2
$$$\dot{W}=w\times \dot{m}$$$
where
$$\dot{W}$$
is the power,
$$w$$
is the work per unit mass, and
$$\dot{m}$$
is the mass flow rate.
Turbines, Pumps, and Compressors are often considered adiabatic (no heat transfer), so in a steady-state and steady-flow conditions:
$$$h_{in}=h_{exit}+w$$$
where
$$h$$
is specific enthalpy, and
$$w$$
is the work per unit mass. Per the problem statement’s figure:
$$$w_{turbine}=h_3-h_4=3,500-2,500=1,000\:kJ/kg$$$
Thus, to get the power produced by the turbine:
$$$\dot{W}=w_{turbine}\times \dot{m}=1,000\frac{kJ}{kg}\times 25\frac{kg}{s}=25,000\:kW=25\:MW$$$
25 MW
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked
Similar Problems from FE Sub Section: Steady-Flow Systems
225. Boiler Pump
250. Rankine Cycle
Similar Problems from FE Section: First Law of Thermodynamics
225. Boiler Pump