Composite Material
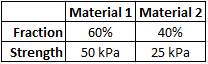
If a composite material has the known characteristics shown, and a measured strain of 0.05, what is its modulus of elasticity?
Expand Hint
$$$\sigma_c=\sum f_i\sigma_i$$$
where
$$\sigma_c$$
is the strength parallel to the fiber direction,
$$f_i$$
is the volume fraction of the individual material, and
$$\sigma_i$$
is the individual material’s strength.
Hint 2
Hooke’s Law:
$$$\sigma=E\varepsilon $$$
where
$$\sigma$$
is the stress,
$$E$$
is the elastic modulus (modulus of elasticity or Young’s modulus), and
$$\varepsilon $$
is the strain.
A composite material is a material formed from two or more “base” materials. The base/basic materials have notably dissimilar physical or chemical properties, but when merged to create a composite, produce properties unlike the individual elements. To find a composite’s strength:
$$$\sigma_c=\sum f_i\sigma_i$$$
where
$$\sigma_c$$
is the strength parallel to the fiber direction,
$$f_i$$
is the volume fraction of the individual material, and
$$\sigma_i$$
is the individual material’s strength. Thus,
$$$\sigma_c=f_1 \sigma_1+f_2\sigma_2$$$
$$$=(0.6)(50kPa)+(0.4)(25kPa)=30kPa+10kPa=40\:kPa$$$
Hooke’s Law:
$$$\sigma=E\varepsilon $$$
where
$$\sigma$$
is the stress,
$$E$$
is the elastic modulus (modulus of elasticity or Young’s modulus), and
$$\varepsilon $$
is the strain. Therefore,
$$$E=\frac{\sigma_c}{\varepsilon}=\frac{40kPa}{0.05}=800\:kPa$$$
800 kPa
Time Analysis
See how quickly you looked at the hint, solution, and answer. This is important for making sure you will finish the FE Exam in time.- Hint: Not clicked
- Solution: Not clicked
- Answer: Not clicked
Similar Problems from FE Sub Section: Composite Strength
319. Composite Strain
407. Composite Modulus
636. Base Material
Similar Problems from FE Sub Section: Mechanical
004. Stress and Strain
007. Aluminum Alloy Graphs
076. Stress vs Strain Curves
167. Material Crack
172. Tensile Test
200. Critical Crack Length
319. Composite Strain
349. Compressibility Modulus
354. Yield vs Ultimate Strength
358. Brittle vs Ductile vs Plastic
407. Composite Modulus
445. Fracture Toughness
455. Fracture Stress
495. Yield and Ultimate Strength
538. Fracture
636. Base Material
653. Goodman vs Soderberg
Similar Problems from FE Section: Composite Materials
319. Composite Strain
407. Composite Modulus
636. Base Material
Similar Problems from FE Section: Properties of Materials
004. Stress and Strain
007. Aluminum Alloy Graphs
076. Stress vs Strain Curves
167. Material Crack
172. Tensile Test
200. Critical Crack Length
319. Composite Strain
349. Compressibility Modulus
354. Yield vs Ultimate Strength
358. Brittle vs Ductile vs Plastic
407. Composite Modulus
445. Fracture Toughness
455. Fracture Stress
495. Yield and Ultimate Strength
538. Fracture
542. Resistivity
544. Conductivity
636. Base Material
653. Goodman vs Soderberg